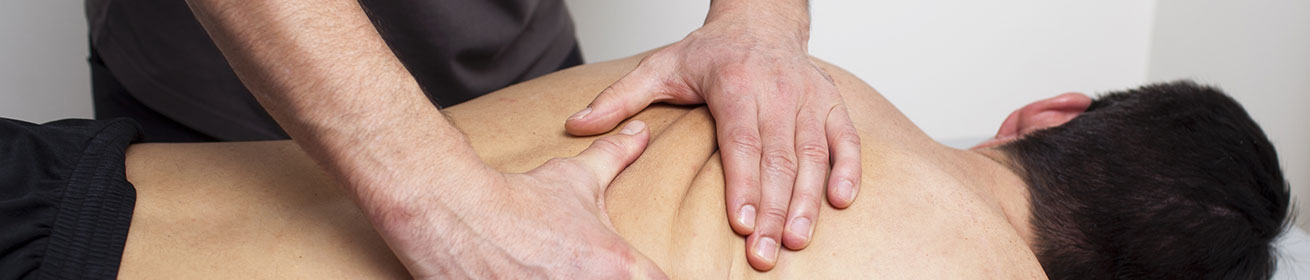
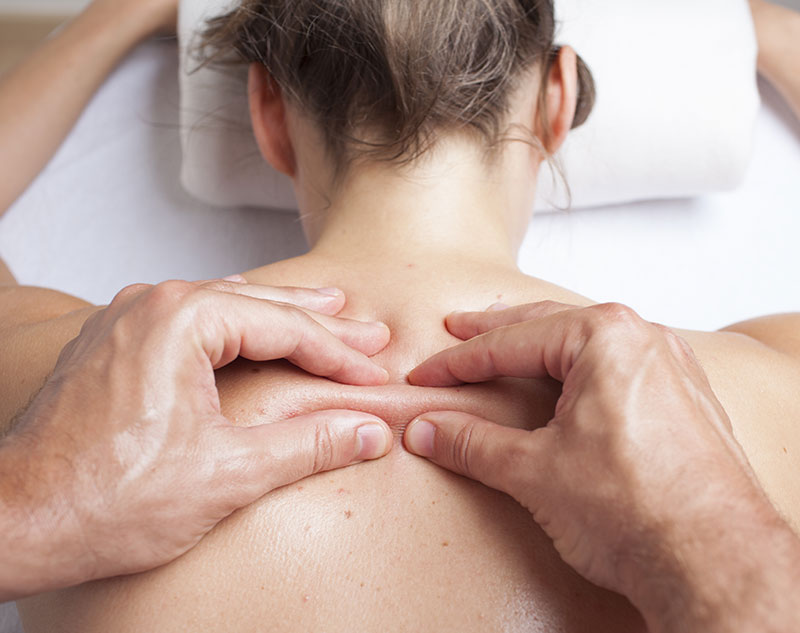
Myofascial therapy is a treatment option that many people are not aware of. It is a form of soft tissue therapy intended for pain relief and increasing range of motion. Myofascial therapy can be used in treating a variety of conditions such as back pain, chronic fatigue syndrome, back pain, poor posture, carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, scoliosis and tennis elbow. It works by stretching and loosening the fascia so that it and other contiguous structures can move freely so as to restore normal function and mobility. The term myofascia is derived from the latin words (muscle-Myo) and (band- Fascia). Fascia is the soft tissue component of connective tissue that provides support and protection for most structures in the body including the organs as well as the muscles. It also plays a major role in maintaining normal metabolic processes.
Office Hours
Monday | 8:00am – 6:00pm
Tuesday | 8:00am – 2:00pm
Wednesday | 8:00am – 6:00pm
Thursday | 12:00pm – 6:00pm
Friday | 8:00am – 2:00pm